数组排序
LeetCode原题
难度 中等
给你一个整数数组 nums,将该数组升序排列。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [5,2,3,1]
输出:[1,2,3,5]
示例 2:
输入:nums = [5,1,1,2,0,0]
输出:[0,0,1,1,2,5]
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 50000
-50000 <= nums[i] <= 50000
这道题在LeetCode中难度是中等,可能看上去很简单,因为我们随手可以写出的排序算法就有很多种,但是如果想要牢靠掌握所有的排序算法还是够得上中等难度的。
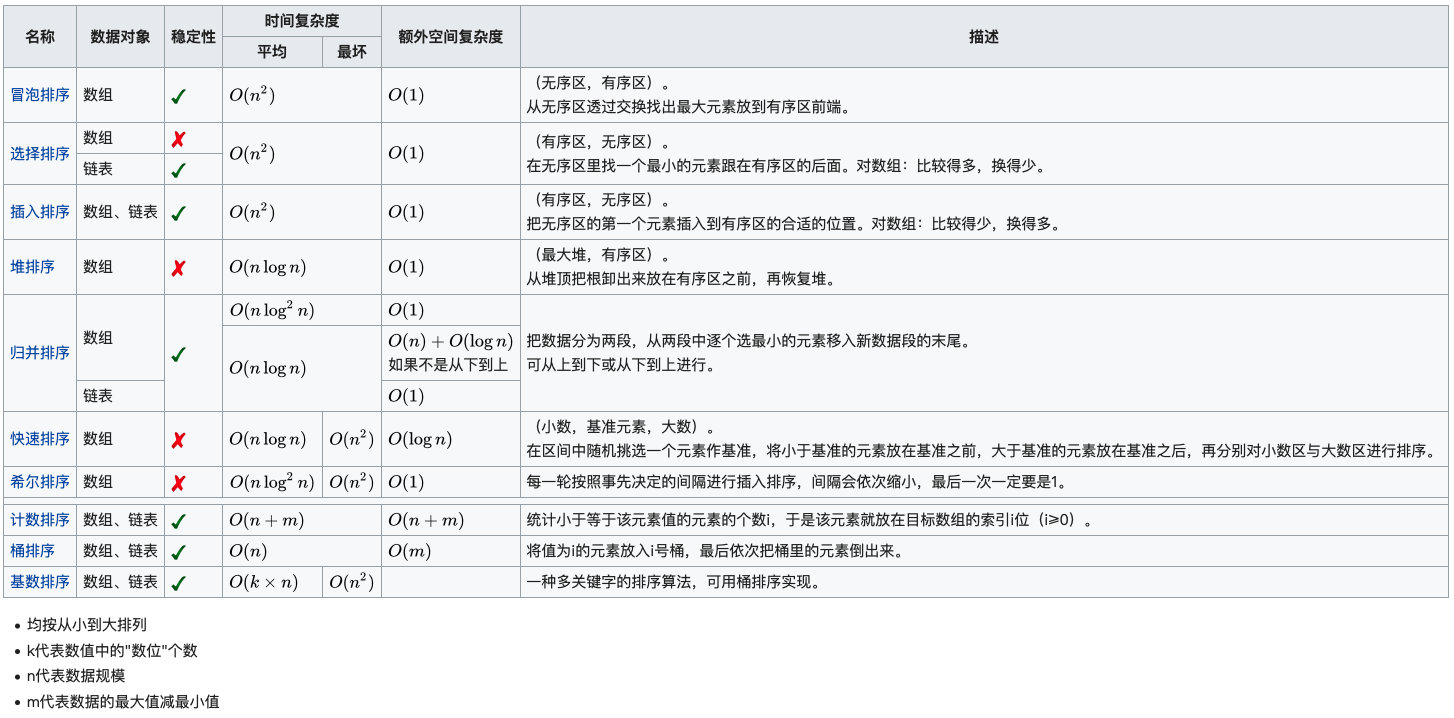
下面是几种常用算法的整理:
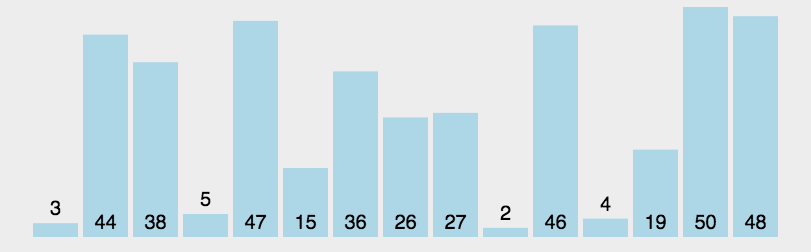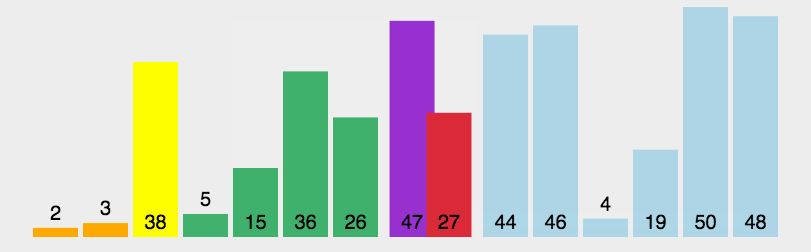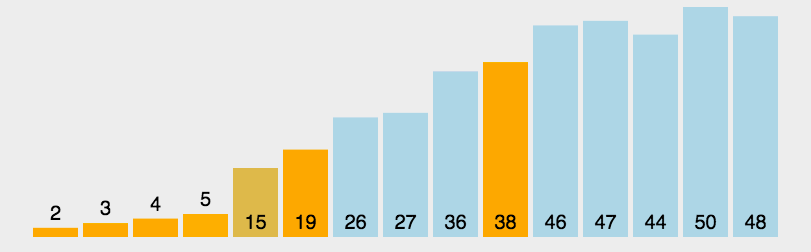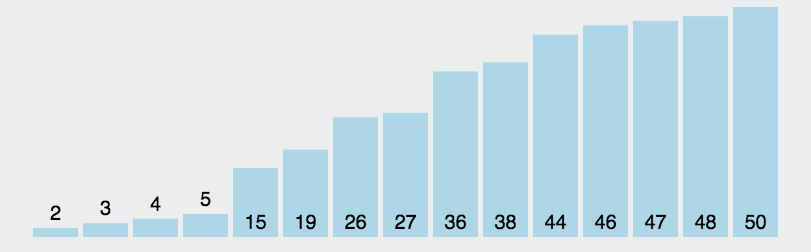
快速排序
快排是最常用的几种排序方法之一,其主要方法是
在
数组中随机选择一个数作为基准,将该基准放到数组的末端。将数组中所有数与基准进行对比,将大于基准的数移动至基准的右侧。
将数组左侧和右侧分别试做两个新数组重复步骤1。
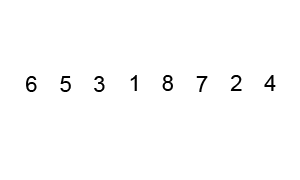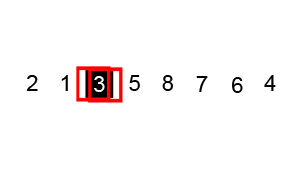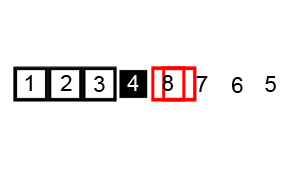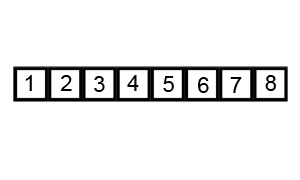
1 | class Solution: |
归并排序
归并排序的主要思想是递归+重排两个有序数组
将数组分成两个部分数组,对返回的两个有序数组进行排序
如果部分数组中只有一个元素,直接返回,否则进行步骤1
对两部分分别进行merge,返回排序后的数组
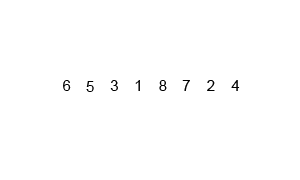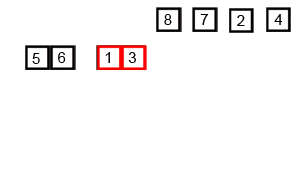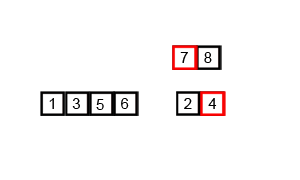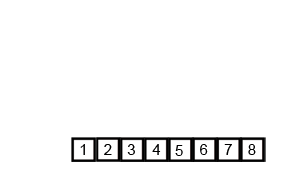
1 | class Solution: |
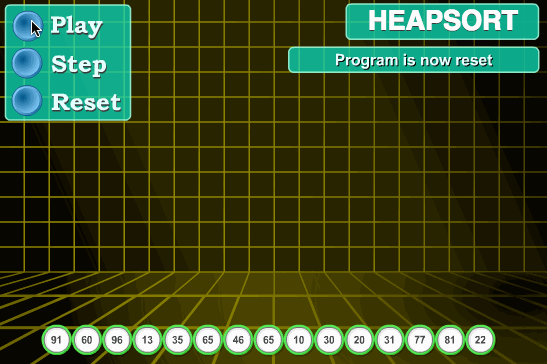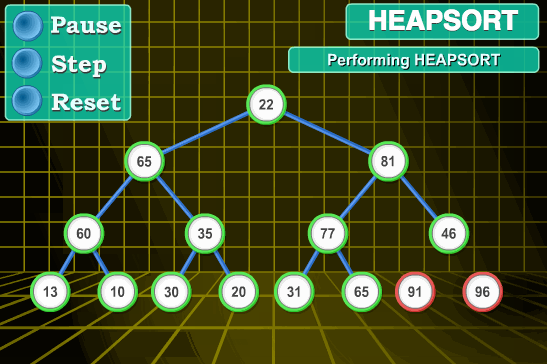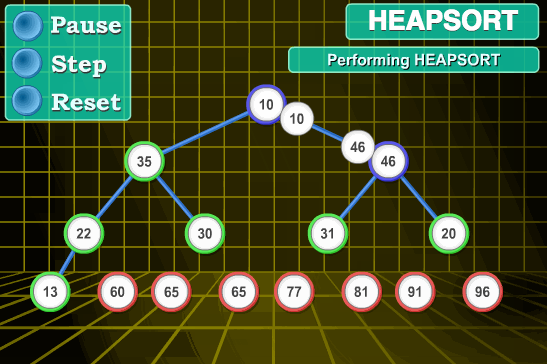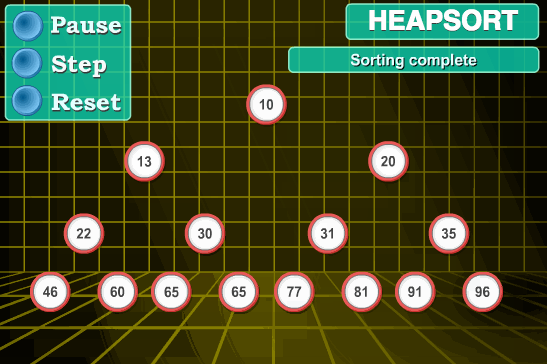
堆排序
堆排序是基于堆这种数据结构所设计的排序算法
建堆,从底向上调整堆,使得父亲节点比孩子节点值大,构成大顶堆
交换堆顶和最后一个元素,重新调整堆。

1 | def heap_sort(nums): |